Lens

return to previous page
LENS
Congenital Cataracts
Definition : – A cataract is an opacity of the lens.
Cataracts occur infrequently in childhood but early diagnosis and management is essential
Common Aetiological Factors
Hereditary – Dominant, recessive or x-linked
- Infective – Intrauterine Rubella,
- Cytomegalic Virus
- Metabolic – Diabetes, Galactosaemia
- Trauma
Diagnosis:
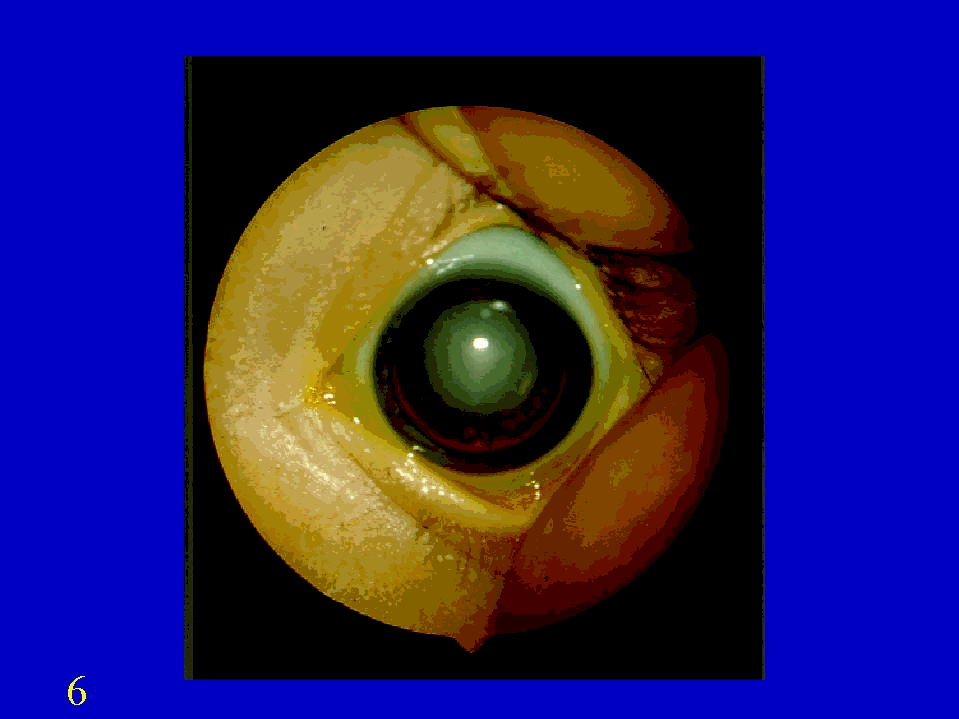
Altered red reflex on ophthalmoscopic examination.congenital cataract ;
This examination is essential, in all infants, in the first week of life.
Management Of Congenital Cataracts
In recent years the importance of early extraction of congenital cataracts has been emphasized. Dense cataracts cause dense deprivational amblyopia. If relatively normal foveal vision is to be obtained these cataracts must be extracted and vision corrected with appropriate lenses by 3 months of age if possible. This management today includes simultaneous cataract extraction and implantation of an intraocular lens. Early DIAGNOSIS, SURGERY and CORRECTIVE LENSES are essential for good vision.
Unilateral Cataracts present a major problem of anisometropia. Again early extraction, correction with Intraocular lens, contact lens together with therapy to overcome deprivational amblyopia results in an occasional moderate visual result. But, the road is long and difficult for the child, the parent and the physician! Surgery for unilateral cataracts should not be recommended lightly.
Note: Examine all neonates for cataracts. Extract and refract by 2 months.
Management of congenital Cataract
Dislocated (Subluxated)Lenses
If the Lens zonule (ligament which holds the lens in place) is disturbed dislocation partial or complete may occur.
This results in reduction of vision and sometimes secondary glaucoma. Lens dislocation may occur following trauma but it is associated with a number of systemic conditions- Marfan's Subluxated lens
MARFAN’S S
MARCHESANI’S SYNDROME
EHLERS-DANLOS’ SYNDROME
HOMOCYSTINUREA
SULFITE OXIDASE Deficiency